>
Circular House
Madrid, Spain
2018 - 2019
Architectural design, urban and property research: Husos + elii
Business plan, management and social innovation model and property research: Ultrazul
Client: Fundación Daniel y Nina Carasso.
Composition of knowledges and circularity
This
is one of the two building prototypes commissioned by the Carasso Foundation
for its future headquarters in Madrid. It is part of a first commission for a
Feasibility Study. This study is a «360-degree design» carried out by a large
multidisciplinary team coordinated by two groups: Contenedor (architectural project)
and Contenidos (development of the economic, management and social innovation
model). Both groups were also responsible for coordinating the urban and real
estate research to carry out the project. The building must accommodate
different agents and uses linked to the Foundation's main lines of action:
sustainable food (hereinafter SF) and citizen art (CA). The objective is to
build a model building in terms of social, economic and environmental
sustainability, designed under the principles of circularity.
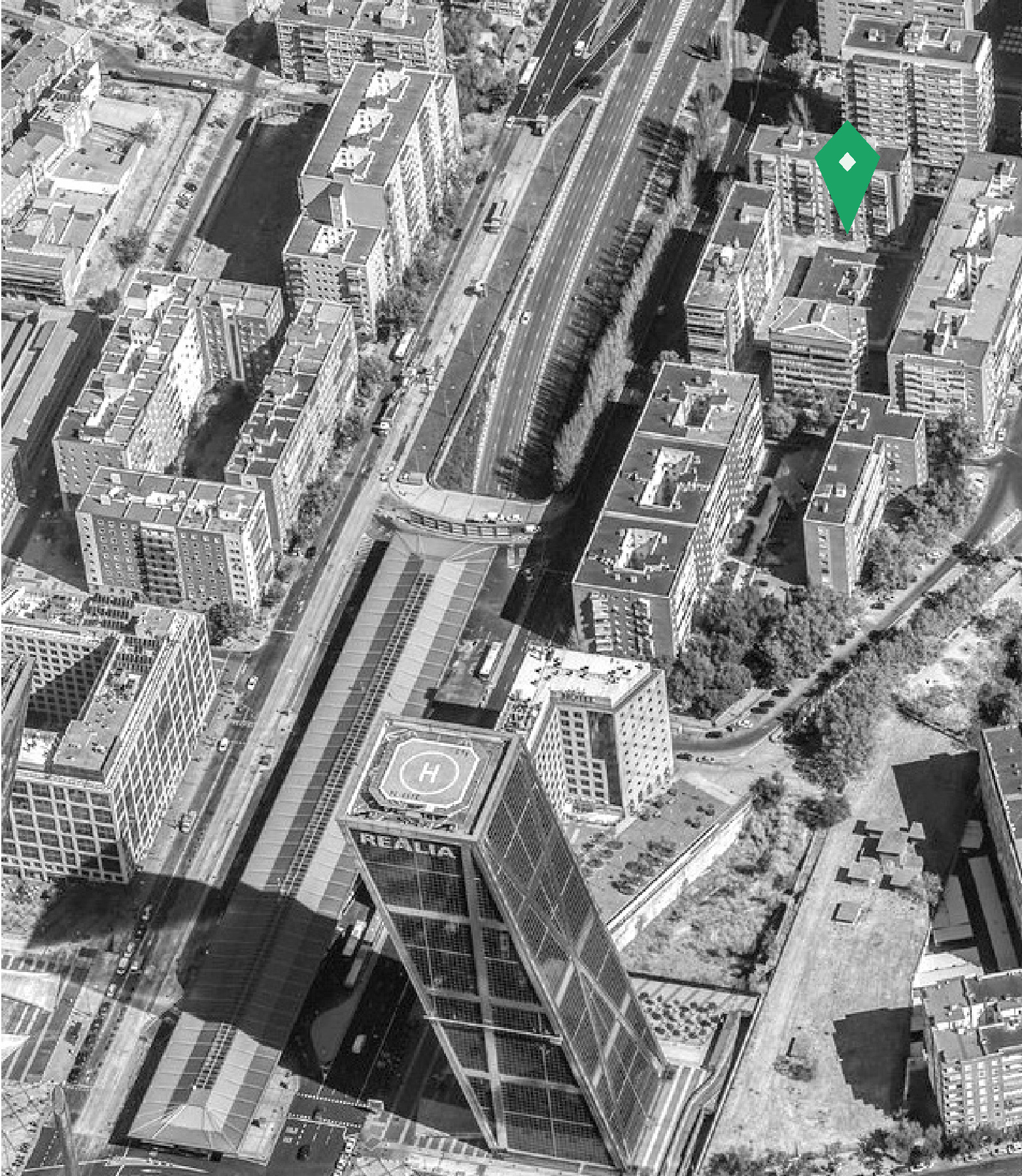
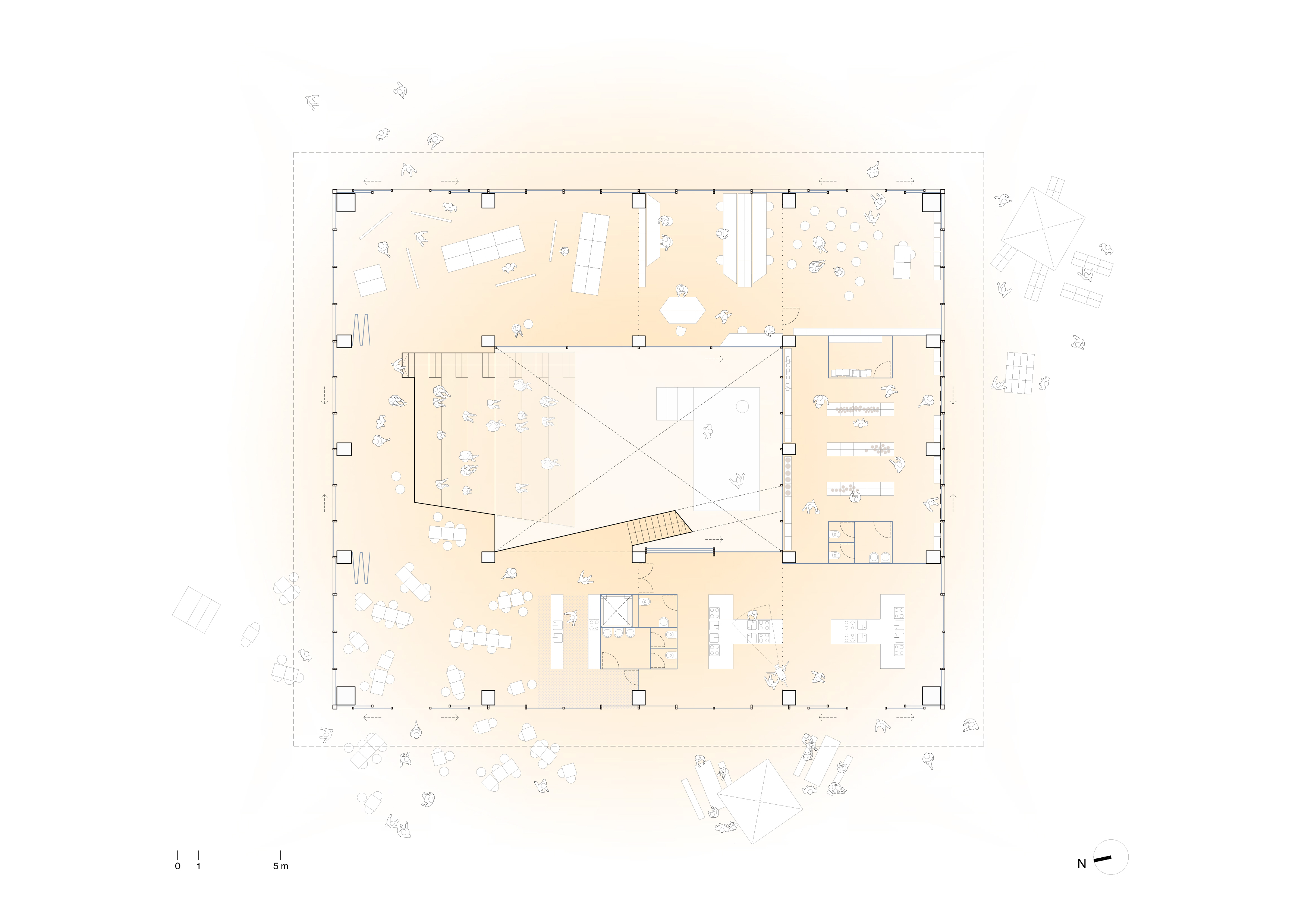
Instead
of building from scratch, we propose to reuse and rehabilitate an empty
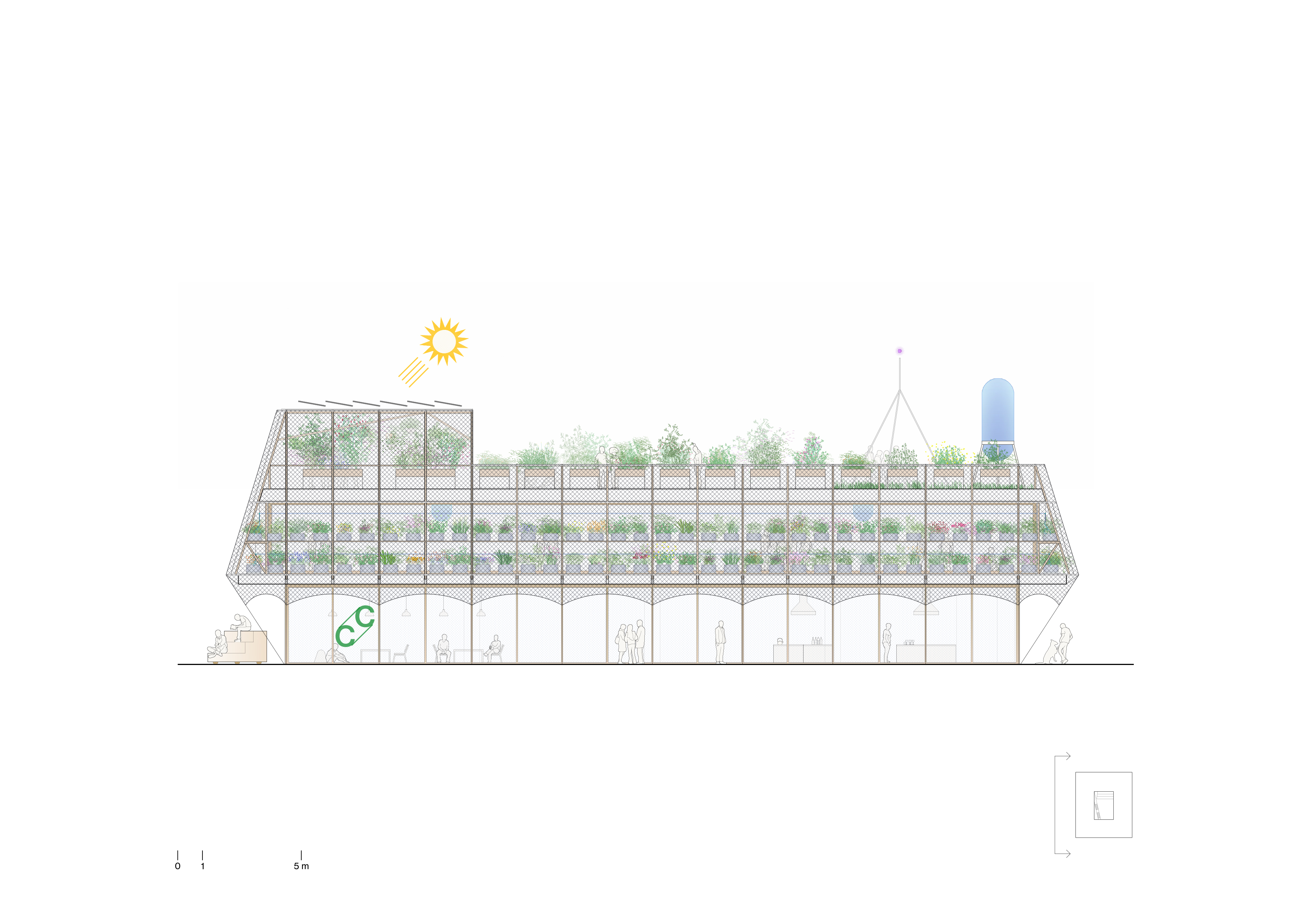
building. This building is located near the Paseo de la Castellana. It is a
two-story building of 29 x 33 meters with a large walkable roof. Its extensive
roof and its horizontal proportion make it possible to have a large shared
green space on the outside, but also pose the challenge of solving the problem
of natural and direct lighting and ventilation inside the building. For this
reason, one of the first decisions in the project is to open a large
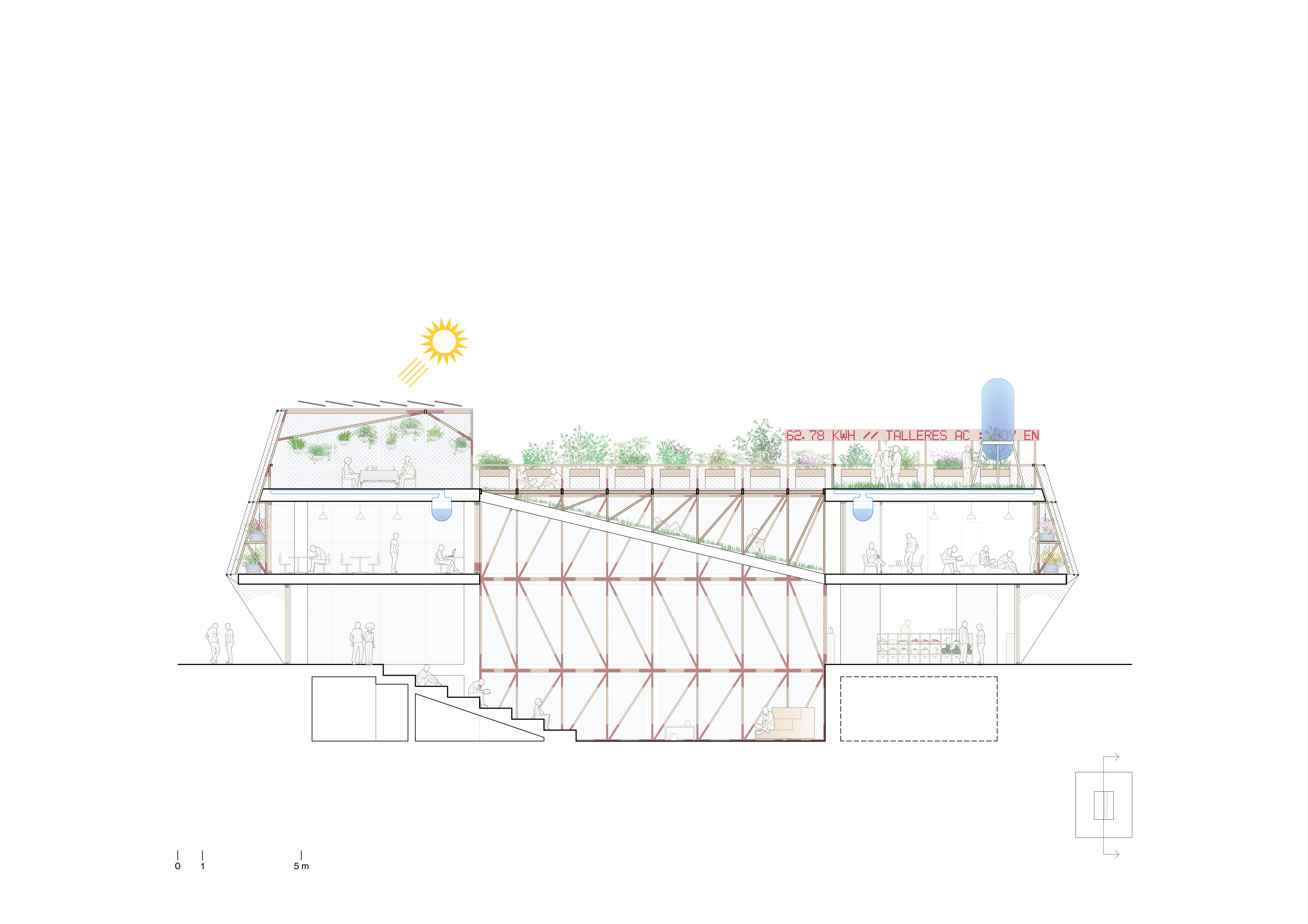
courtyard-atrium in the heart of the structure, to allow the passage of light.
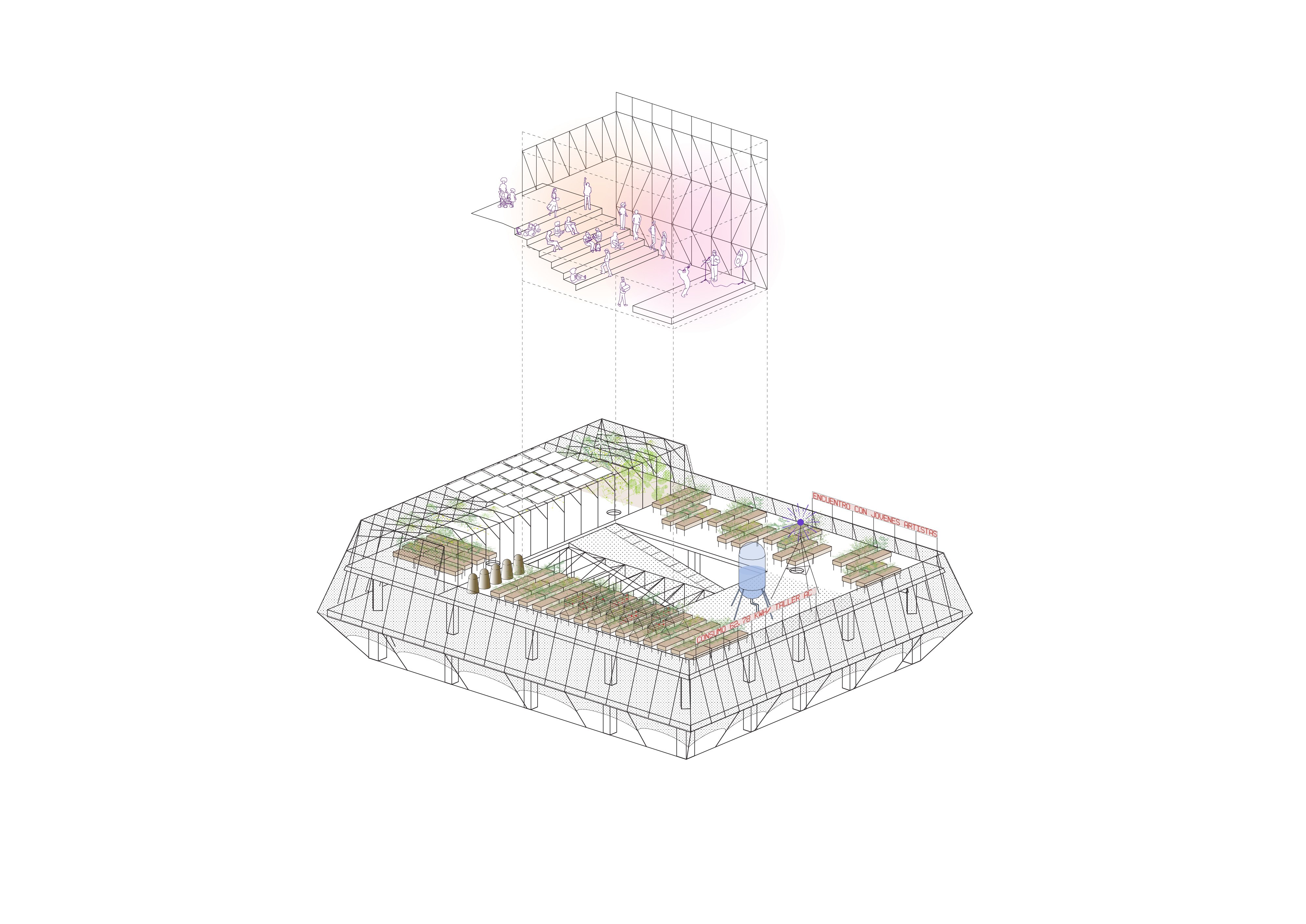
The central courtyard is the core of the activities of the CA, although it will
also serve as a multipurpose stage for different types of events and uses
linked to the SF, and to other communities that will have a place in the house.
The courtyard is the connecting element of the whole house.

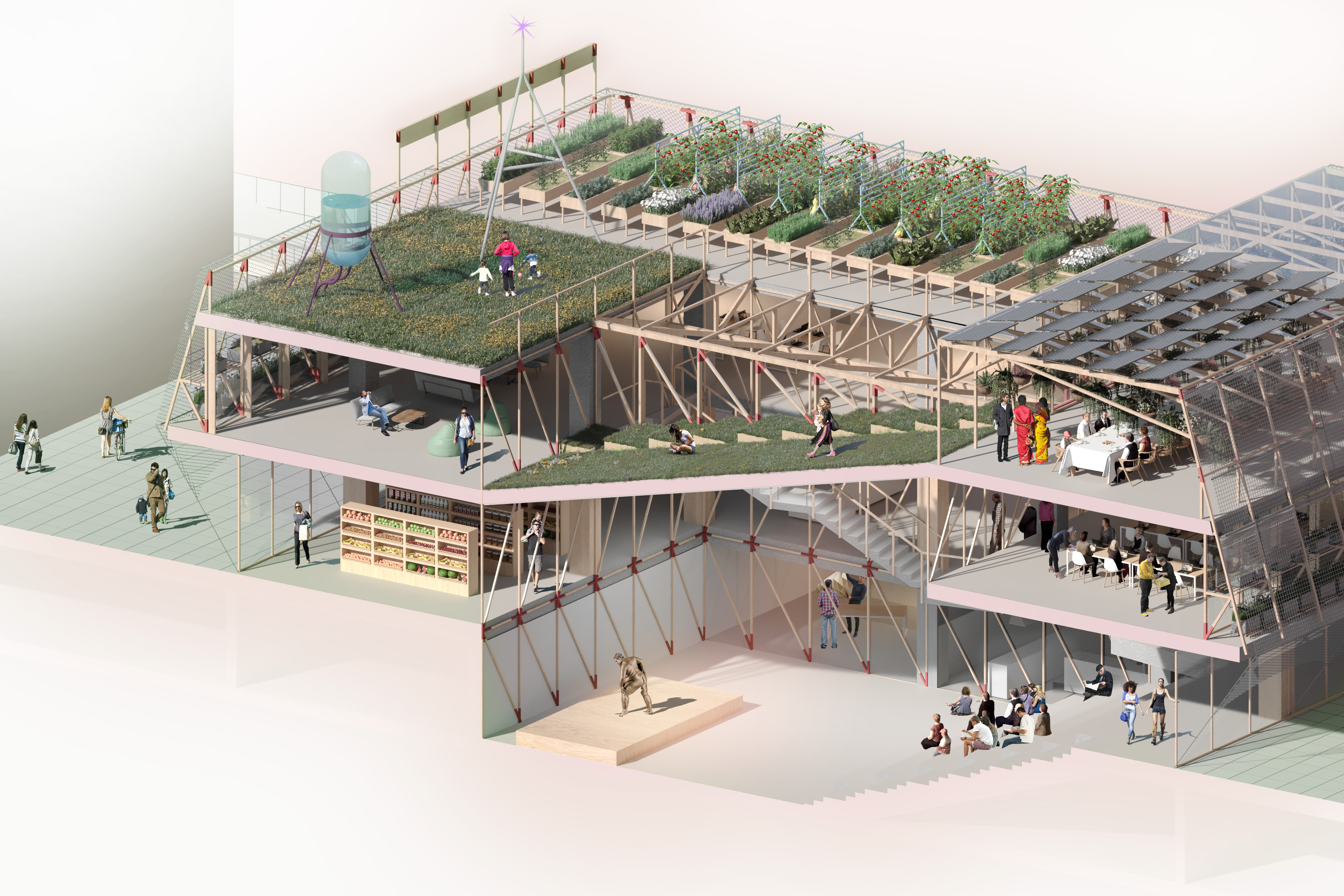
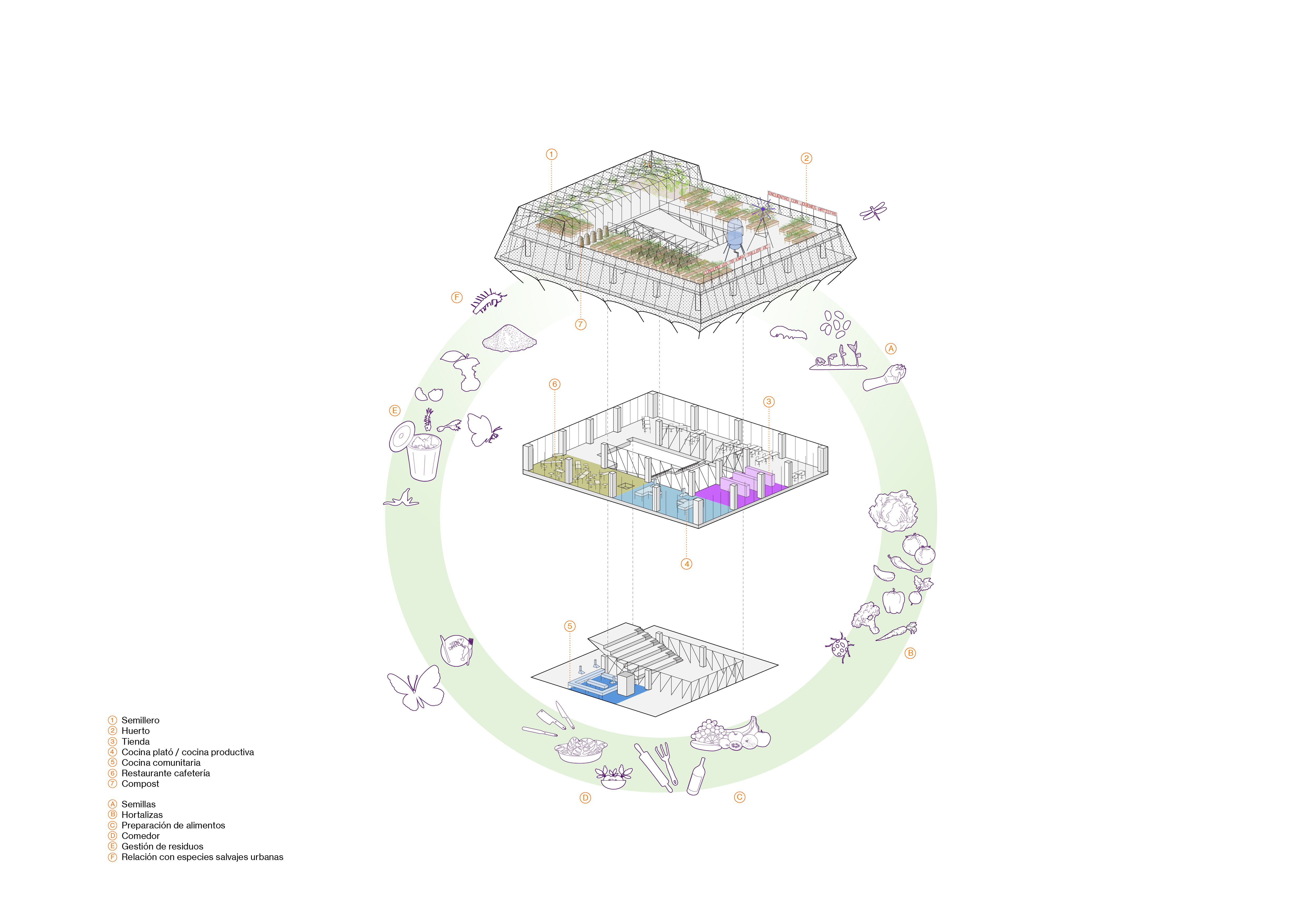
A food
circuit is organized around a terrace-garden, which is completed with a
greenhouse, different types of experimental and training kitchens, an organic food
market, compost bins and other facilities related to the SF. Between these two
areas, terrace and courtyard, different types of spaces dedicated to
collaborative work are distributed within the building. The spaces closer to
the SF and those more linked to the CA are closely related, encouraging
exchanges from one area to the other, following the desire of the Carasso
Foundation to promote the «composition of knowledges» within the building.
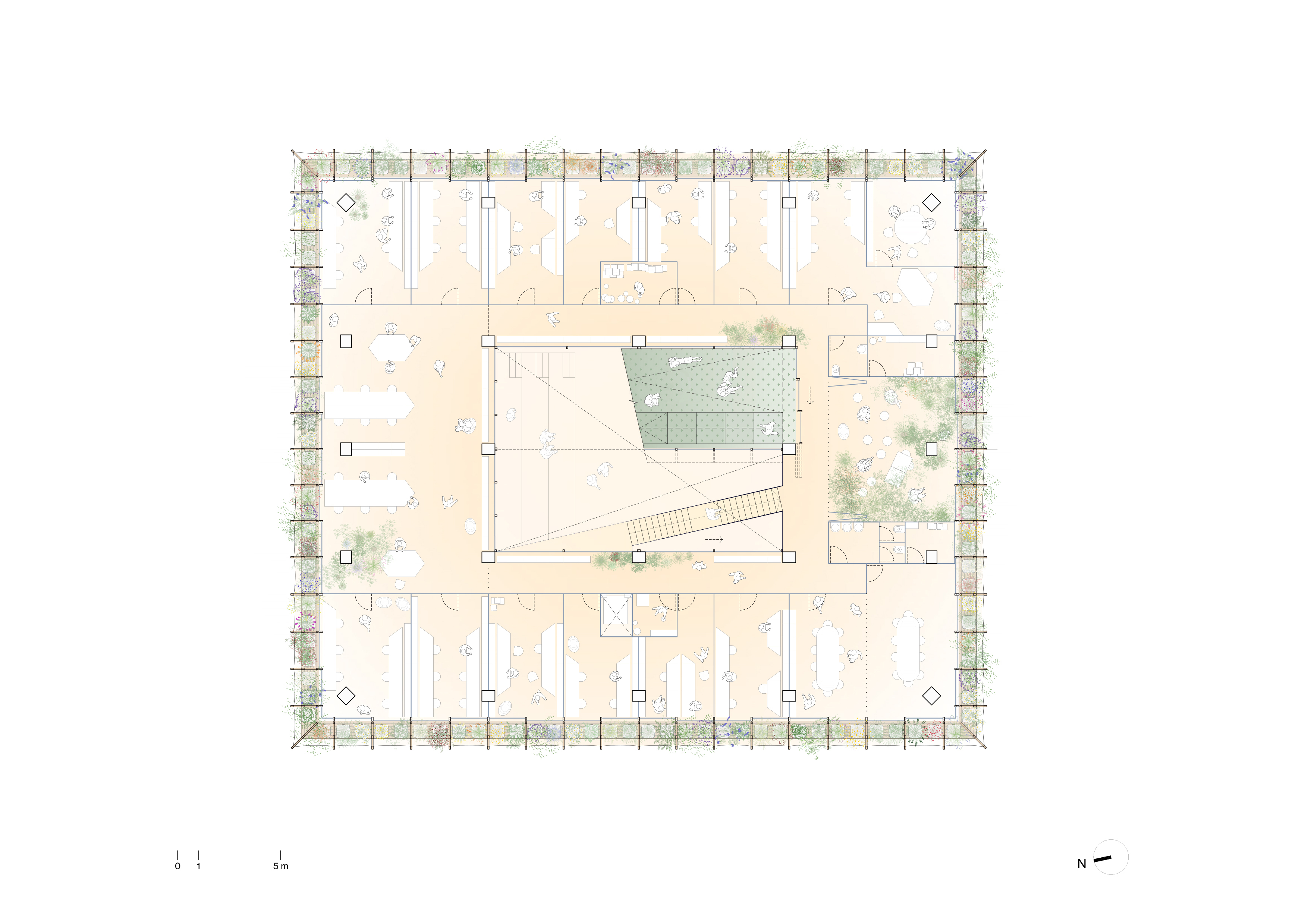
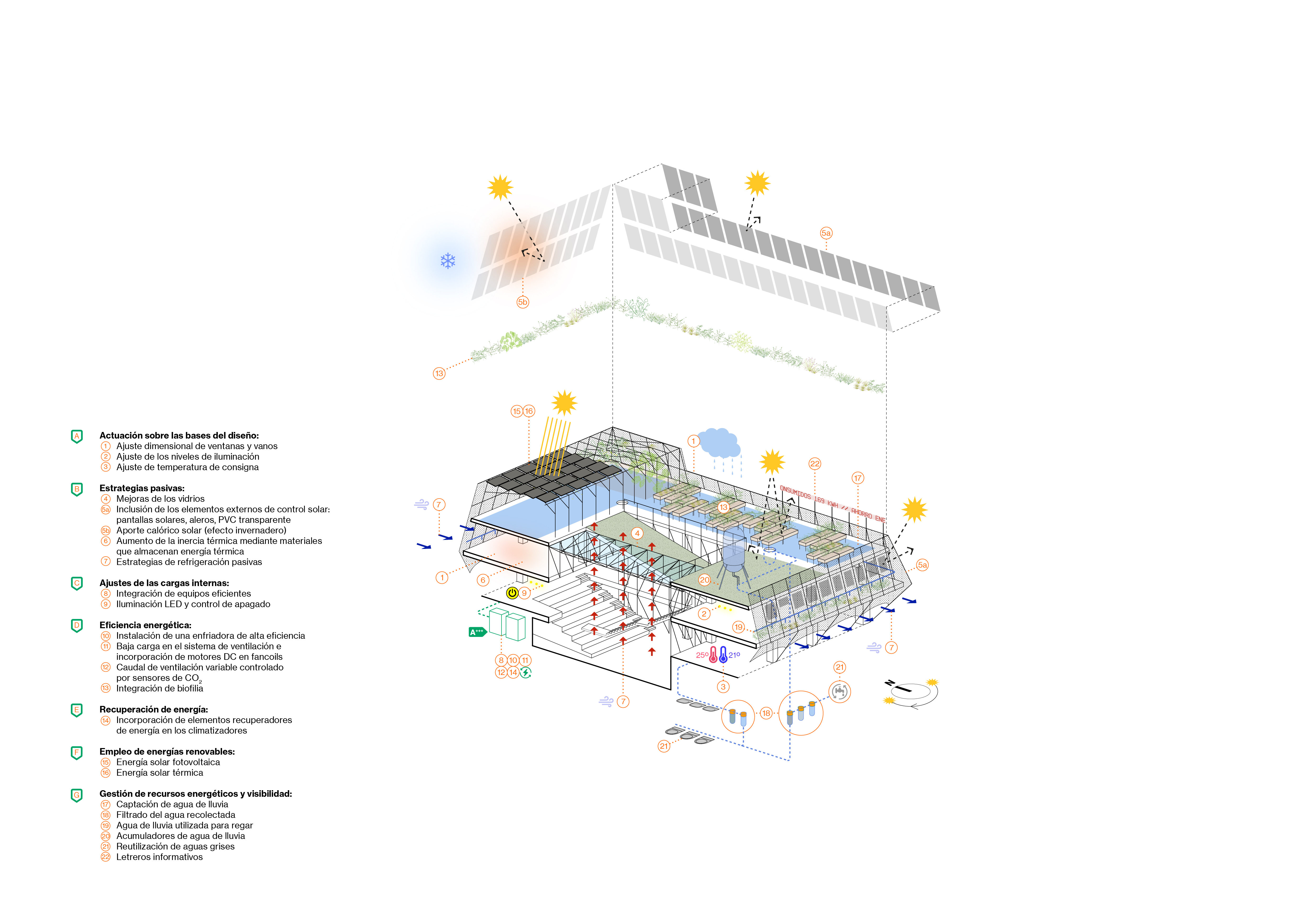
Bioclimatic roof and facade
A
vegetable floor on the garden terrace protects the building on its upper face,
both in winter and summer. On its sides, a bioclimatic facade acts as a thermal
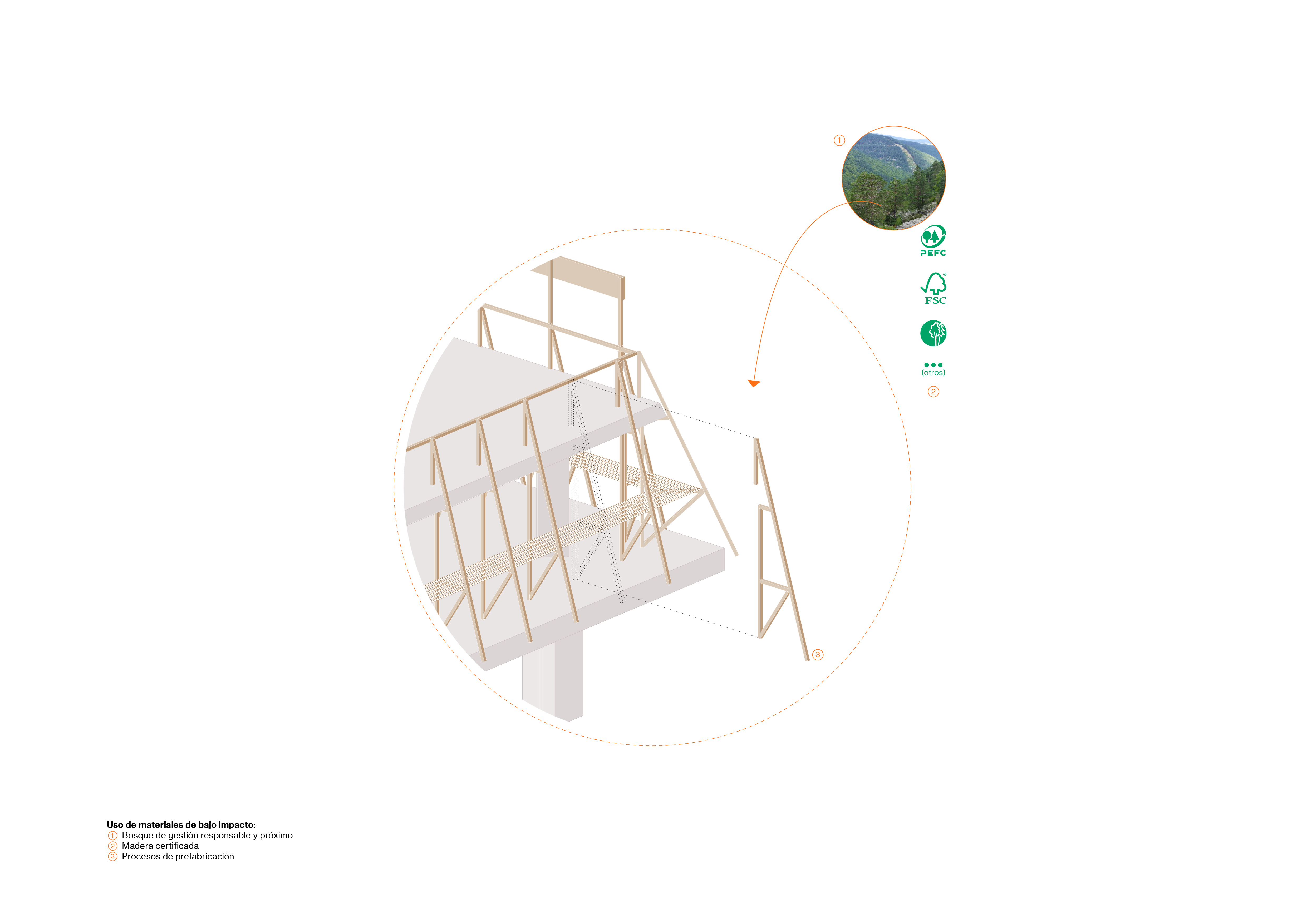
regulator. The outer layer consists of a wooden structure from responsibly
managed forests. It supports a vertical garden with pots made of recycled PET
felt. This structure is surrounded by a mesh of tensioned steel cables and a
series of awnings to control solar incidence in summer, with different opacity
treatments in its different facades. Its interior layer consists of glazed
sliding doors and wooden carpentry.
![]()
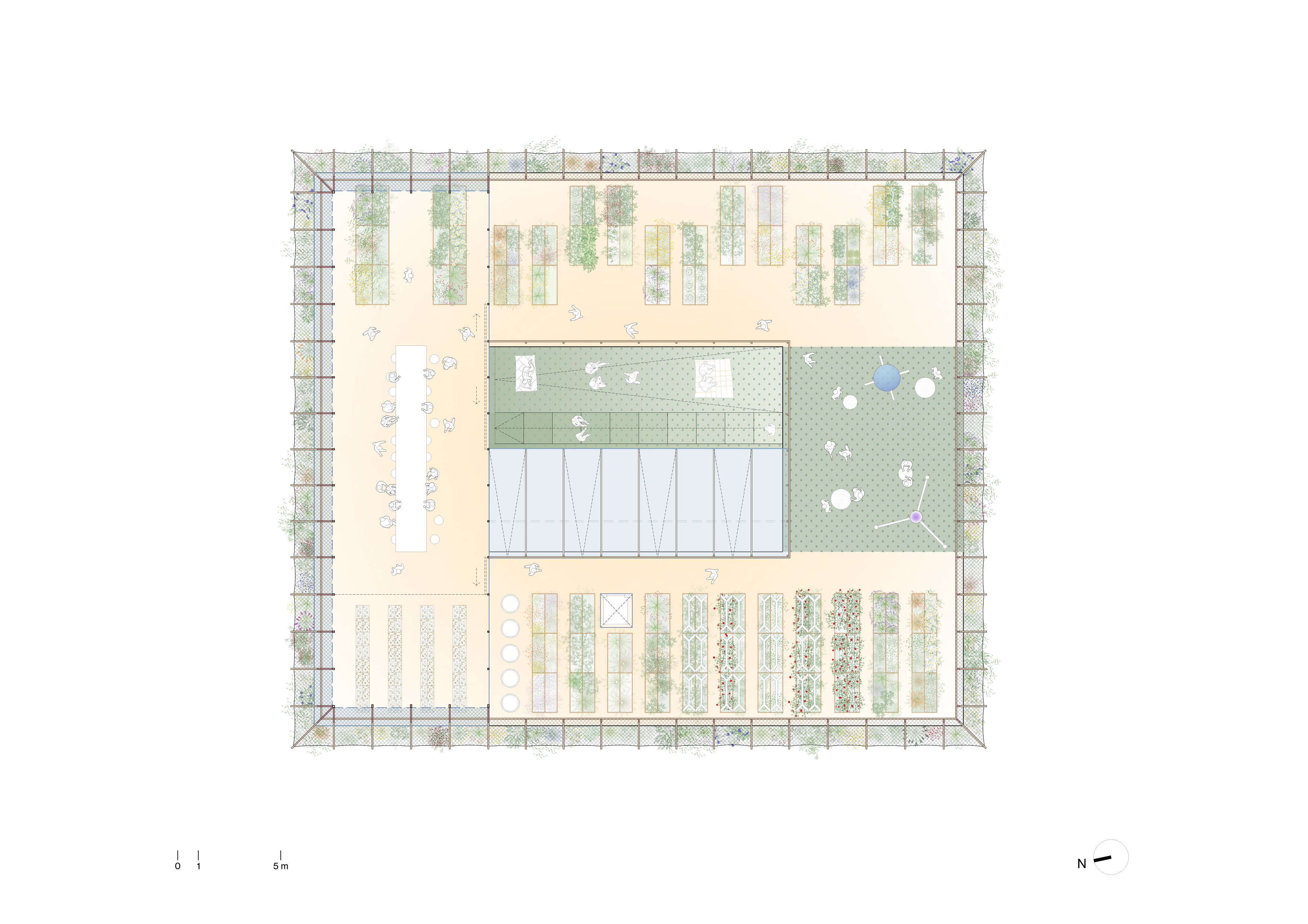
20 environmental actions
As
part of the goal of achieving a near-zero consumption building, a total of
twenty environmental actions are proposed. In addition to those already
mentioned, the following are highlighted, for example: rainwater and gray water
reuse circuits, adjustment of setpoint temperatures, incorporation of
low-energy impact materials according to their life cycle, lighting control
through the installation of focal lights instead of ambient lighting, and
photo-voltaic and solar panel systems. All this forms an energy landscape with
indicators that make its management visible. Together with the food circuit, we
tried to create a garden building with a didactic and at the same time playful
resource management.